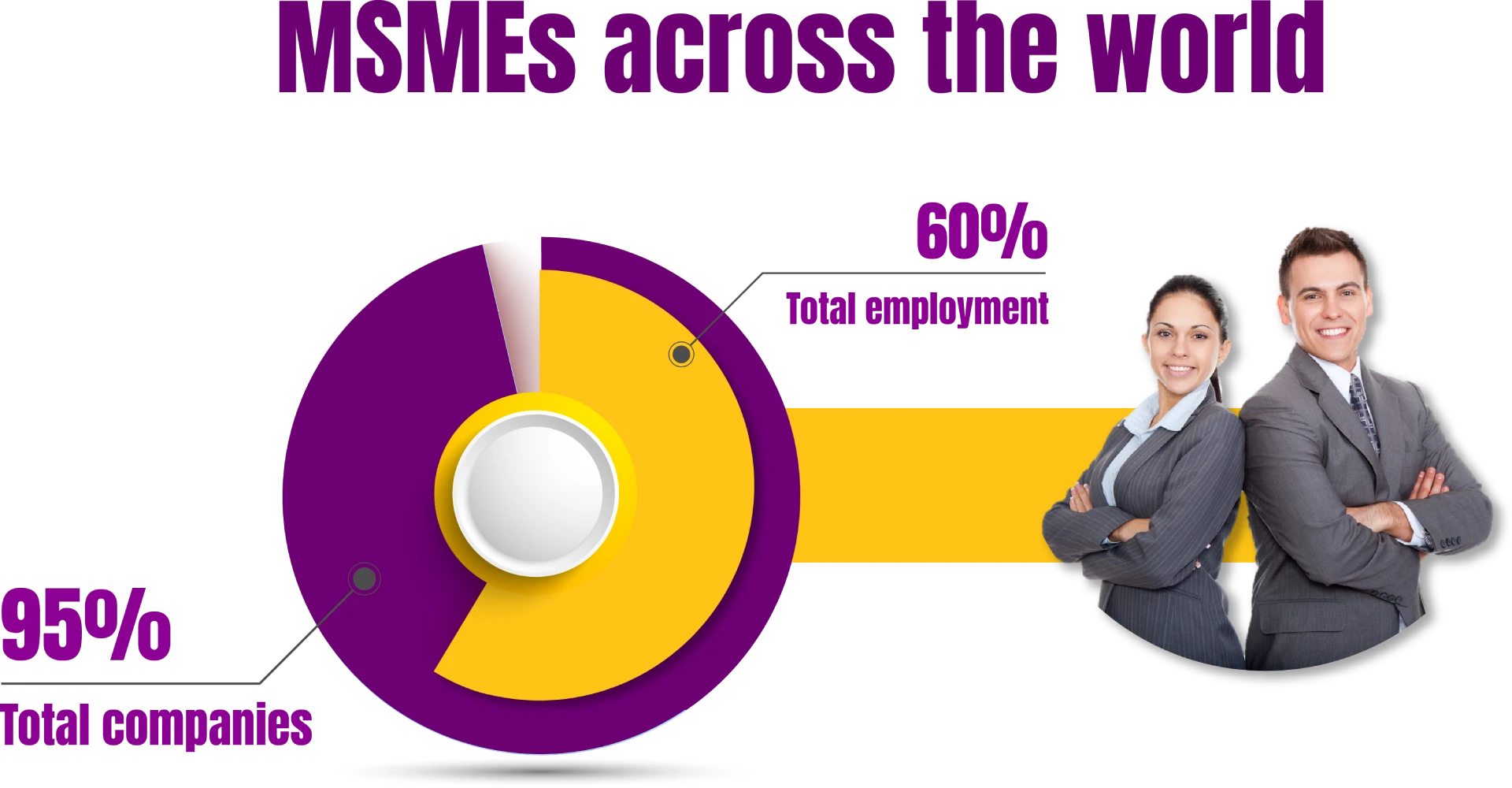
Digital transformation is creating new opportunities for entrepreneurs around the world. It is enabling traditional businesses to evolve, new business models to emerge, and digital entrepreneurship to flourish. Although most digital businesses are still small and local, digitalization is creating opportunities for MSMEs to expand their reach internationally. This is important because MSMEs account for the majority of businesses and employment in the world.
E-commerce has the potential to diversify the scope and geographical reach of trade for developing countries. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an increase in the use of digital solutions, including e-commerce, as people have been forced to stay home and avoid social interaction. This has boosted demand for digital services and online shopping, leading more people to make use of digital channels. As a result, the share of e-commerce in global retail trade is estimated to have increased from 16% in 2019 to 19% in 2020 and has remained at that level in 2021.

The rise of e-commerce has created new opportunities for women in developing countries. Digital technologies allow women to work from home, expand their businesses, and reach new markets. This could lead to significant economic growth, with IFC studies estimating that women could add over $14.5 billion to e-commerce markets in Africa and $280 billion in South-East Asia between 2025 and 2030.

Despite the potential opportunities that e-commerce offers women, there are still significant disparities between women entrepreneurs and women workers in terms of their ability to take advantage of these opportunities. Women are underrepresented in the global workforce, with only 47% of women participating in labor markets compared to 72% of men. This difference is even more pronounced in some regions, reaching up to 50 percentage points. In terms of leadership and decision-making, gender disparities are also significant, with women holding only 28% of managerial positions globally in 2019, which is almost the same share as in 1995. The World Bank’s most recent Enterprise Survey found that only 18% of surveyed enterprises worldwide had a female top manager.
The gender gap in internet usage has narrowed globally, but it remains significant in many developing countries. For example, in Europe, 85% of women used the internet regularly in 2020, compared to 87% of men. However, in Africa, only 24% of women used the internet, compared to 35% of men. And in the least developed countries (LDCs), only 19% of women used the internet, compared to 31% of men. These discrepancies in internet usage continue to be a major barrier to women’s meaningful participation in the digital economy.

Women are less likely to have the advanced technology and digital skills that are necessary to participate fully in the digital economy. This is because they are underrepresented in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education and in STEM-related jobs. For example, only 35% of STEM students in higher education globally are women and only one in five ICT specialists are women. This lack of opportunity in STEM fields is a major barrier to women’s participation in the digital economy.

Digital entrepreneurship can help women in developing countries participate in the digital economy and reduce gender inequality. However, women entrepreneurs face many obstacles, such as a lack of access to technology, education, and finance. To help more women succeed in digital entrepreneurship, we need to address these obstacles and provide them with the support they need.
This is why UNCTAD launched the eTrade for Women initiative in 2019 to empower women digital entrepreneurs in developing economies. The eTrade for Women initiative provides women entrepreneurs with access to technology, training, and finance. It also helps them to connect with other women entrepreneurs and to access markets.
The eTrade for Women initiative is a valuable resource for women entrepreneurs in developing countries. It is helping them to overcome the obstacles they face and to succeed in the digital economy.
© 2025. All rights reserved by Elicit Research.
